Describe the Involvement of the Membrane in the Cellular Processes
The three functions of the cell membrane are. A phenomenon in walled cells in which the cytoplasm shrivels and the plasma membrane pulls away from the cell wall.

Cell Respiration Sudy Guide B1 Cellular Respiration Cell Respiration Photosynthesis Worksheet
Function of the Cell Membrane.

. The cell membrane is a thin membrane that encases the cytoplasm of the cell and holds the cytoplasm as well as the cells organelles within it separating the interior of the cell from the outside environment. It is also simply called the cell membrane. Occurs when the cell loses water to a hypertonic environment facilitated diffusion the passage of molecules or ions down their electrochemical gradient across a biological membrane with the assistance of specific transmembrane transport proteins.
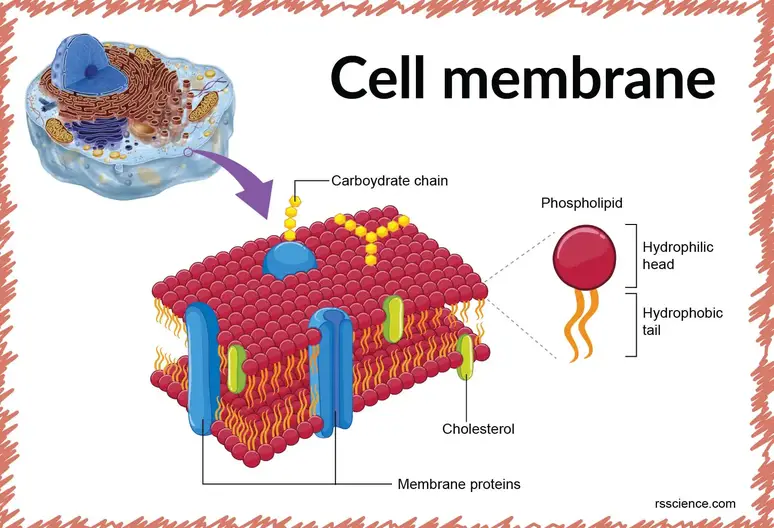
The cell membrane is a delicate organ of the cell which regulates the movement of substances into and outside the cell. Endocytosis takes particles into the cell that are too large to passively cross the cell membrane. The exact mix or ratio of proteins and lipids can vary depending on the function of a specific cell.
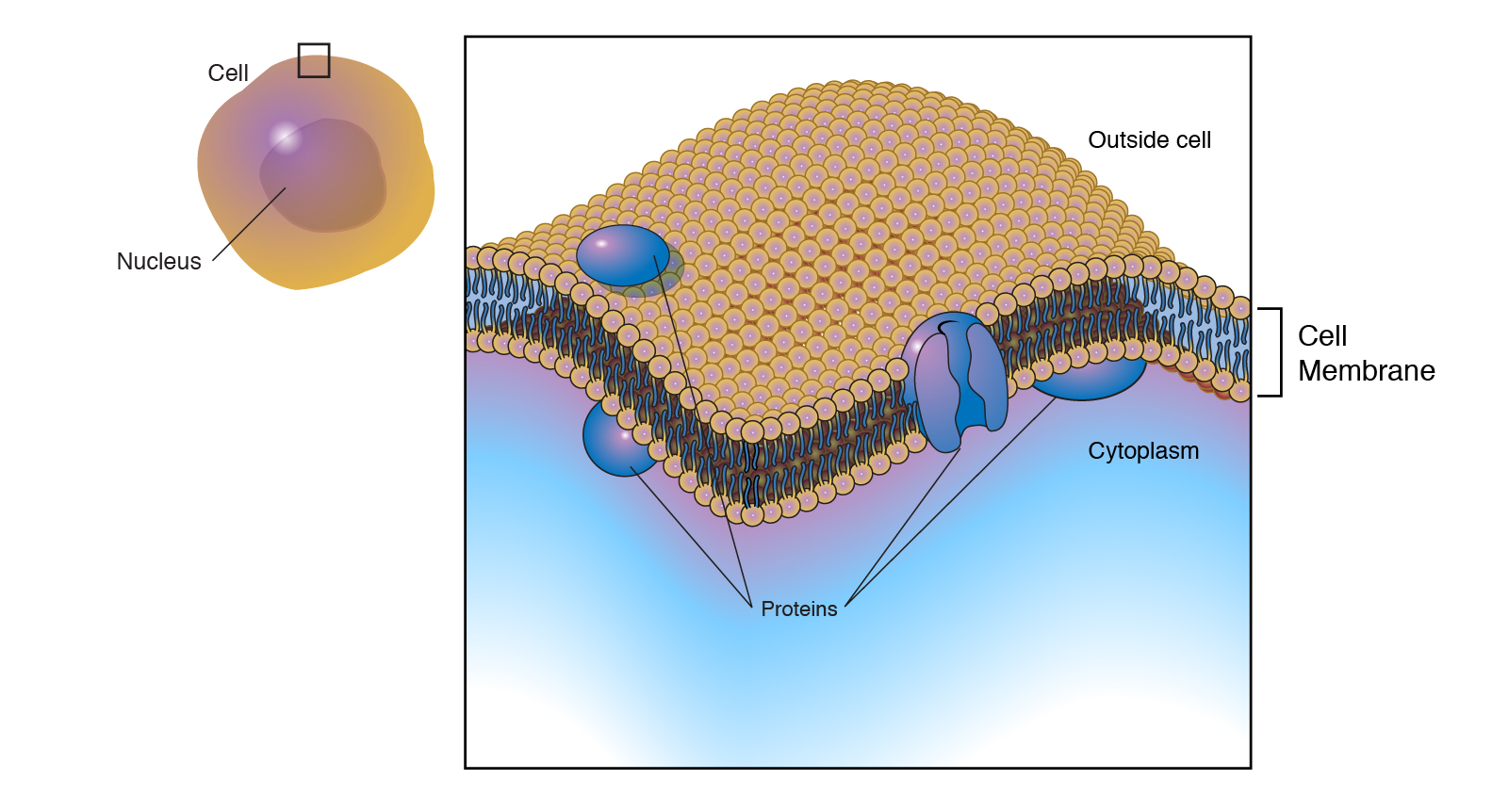
A cells plasma membrane defines the boundary of the cell and determines the nature of its contact with the environment. Receptor-mediated endocytosis uses special receptor proteins to help carry large particles across the cell membrane. It regulates the movement of substances in and out of cells by being selectively permeable to ions and organic molecules.
The cell membrane is a multifaceted membrane that envelopes a cells cytoplasm. Endocytosis bringing into the cell is the process of a cell ingesting material by enveloping it in a portion of its cell membrane and then pinching off that portion of membrane Figure 9. The plasma membrane of a cell is a network of lipids and proteins that forms the boundary between a cells contents and the outside of the cell.
It protects the integrity of the cell along with supporting the cell and helping to maintain the cells shape. It lets some substances pass through rapidly and some substances pass through more slowly but prevents other substances passing through it. The cell membrane is important because it separates and protects a cell from its surroundings.
And 3 they separate vital but. The movement of substances across the membrane can be either passive occurring without the input of cellular energy or active requiring the cell to expend energy in transporting it. Once pinched off the portion of membrane and its contents becomes an.
The plasma membrane also called the cell membrane is the membrane found in all cells that separates the interior of the cell from the outside environment. The plasma membrane consists of a lipid bilayer that is semipermeable. Bulk transport phagocytosis and pinocytosis Cell Membrane Transport.
The cell membrane plays a role in the transmission of impulses in nerve cells. This cell membrane provides a protective barrier around the cell and regulates which materials can pass in or out. Explore the role of.
Think of it as a gatekeeper guardian or border guard. The role of the plasma membrane is to protect the cell from its surroundings. 1 they keep toxic substances out of the cell.
In bacterial and plant cells a cell wall is attached to the plasma membrane on its outside surface. Phagocytosis is the taking in of large food particles while pinocytosis takes in liquid particles. Cells of the stomach and pancreas produce and secrete digestive enzymes through exocytosis.
This allows the intracellular conditions of a. Despite being only 6 to 10 nanometers thick and visible only through an electron microscope the cell membrane keeps the cells cytoplasm in place and lets only select materials enter and depart the cell as needed. It is semi-permeable and regulates the materials that enter and exit the cell.
Diffusion is the process by which molecules in solution move from an area of higher to lower concentration. The types of carrier-mediated transport are described in Chapter 5. Like a drawbridge intended to protect a castle and keep out enemies the cell membrane only allows certain molecules to enter or exit.
The cell membrane is selectively permeable. The cell membrane also called the plasma membrane is found in all cells and separates the interior of the cell from the outside environment. It is a selectively permeable barrier meaning it allows some substances to cross but not others.
The cell membrane gives the cell its structure and regulates the materials that enter and leave the cell. Process by which a cell takes in a substance by surrounding it with the cell membrane requires ATP exocytosis release of substances out a cell by the fusion of. Just as the outer layer of your skin separates your body from its environment the cell membrane also known as the plasma membrane separates the inner contents of a cell from its exterior environment.
The cell membrane regulates the transport of materials entering and exiting the cell. The vesicle membrane then becomes part of the cell membrane. The cell membrane is selectively permeable and able to regulate what enters and exits the cell thus facilitating the transport of materials needed for survival.
Biological membranes have three primary functions. The structure and function of cells are critically dependent on membranes which not only separate the interior of the cell from its environment but also define the internal compartments of eukaryotic cells including the nucleusand cytoplasmic organelles. The main function of the plasma membrane is to protect the cell from its surrounding environment.
Endocrine cells produce and secrete hormones that are sent throughout the body and certain immune. The cell membrane is semi-permeable meaning that it allows certain substances to move into the cell while it keeps certain other substances out of the cell. The cell membrane consists of a lipid bilayer that is semipermeable.
Cells exclude some substances take in others and excrete still others all in controlled quantities. When the vesicle membrane fuses with the cell membrane the vesicle releases it contents into the interstitial fluid. A semipermeable cell membrane allows for cell communication or signaling.
The formation of biological membranes is based on the properties of lipids and all cell membranes. With this type of transport the net rate of solute flux is. Proteins and lipids are the major components of the cell membrane.
2 they contain receptors and channels that allow specific molecules such as ions nutrients wastes and metabolic products that mediate cellular and extracellular activities to pass between organelles and between the cell and the outside environment. The processes that determine molecular movement across membranes are diffusion pinocytosis carrier-mediated transport and transcellular transport. Plasma membranes enclose the borders of cells but rather than being a static bag they are dynamic and constantly in flux.
This semipermeability or selective permeability is a result of a double layer bilayer of. The cell membrane transport occurs in two major ways like. She has taught college level Physical Science and Biology.
Cell Membrane Definition Structure Function And Biology

No comments for "Describe the Involvement of the Membrane in the Cellular Processes"
Post a Comment